
In today’s cloud-first world, backup is no longer just a checkbox; it’s a core pillar of resilience, compliance, and cybersecurity. Oracle’s Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service (ZDLARS) delivers a fully managed, centralized, and secure backup solution for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) databases.
In this article, we’ll walk through what it is, why it matters, and how to enable it step-by-step.
What Is Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service?
Oracle Corporation offers Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service (ZDLARS) as a managed cloud backup and recovery solution designed specifically for Oracle databases running in OCI.
It provides:
- Always-on encryption (at rest and in transit)
- Backup storage in a separate fault domain
- Automated scheduling and lifecycle management
- Built-in support for governance and compliance standards
- Ransomware resilience with immutability
- Zero data loss protection capabilities
Unlike traditional Object Storage–based backups, ZDLARS is purpose-built for Oracle Database recovery performance and security.
Step-by-Step: Enable Autonomous Recovery Service in OCI
Log in to Oracle Cloud Console
- Navigate to the OCI Console.
- Select your target Database instance.
- Open the Backup Configuration section.
Configure Automatic Backups
- Click Configure Automatic Backups.
- If the database is currently configured to use Object Storage, it will be indicated.
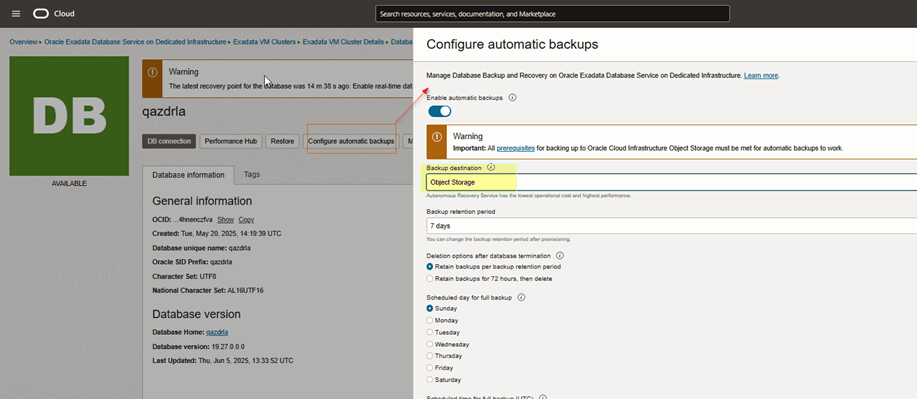
This is where you’ll switch to Autonomous Recovery Service.
Select Autonomous Recovery Service
Under the backup destination options:
- Choose Autonomous Recovery Service
- Select a Custom Retention Policy (recommended for immutability and governance requirements).
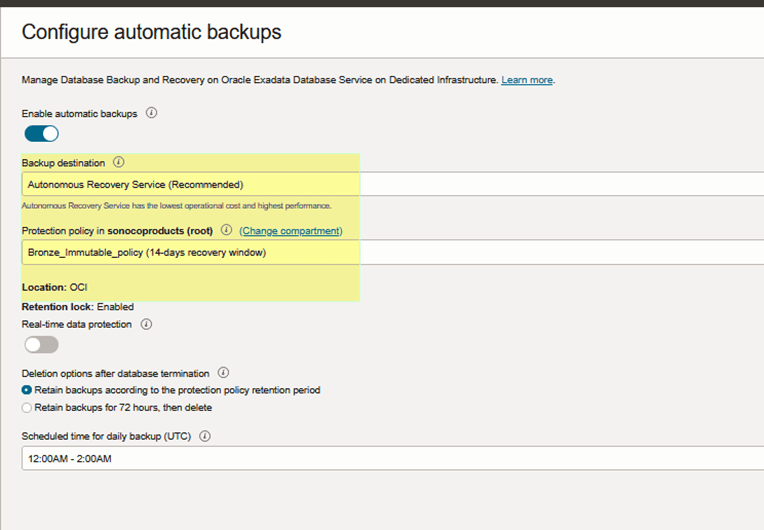
NOTE:
Enabling Autonomous Recovery Service will initiate the first backup immediately. The system will then submit a work request to update the database, which may take a couple of hours to complete.
Verification Steps
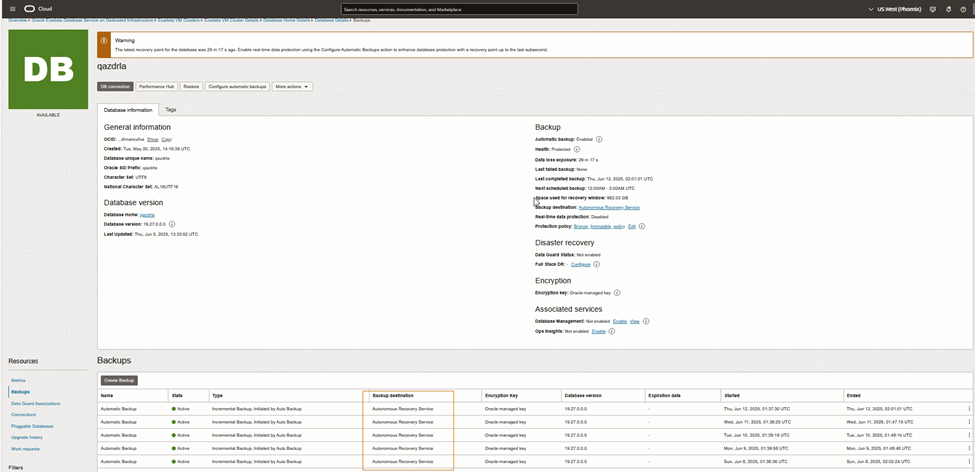
After enabling the service, verify the backup configuration.
Confirm Backup Destination
Verify that:
- Backup destination is updated to DBRS (Previously it may have shown:
backupDestination=oss)
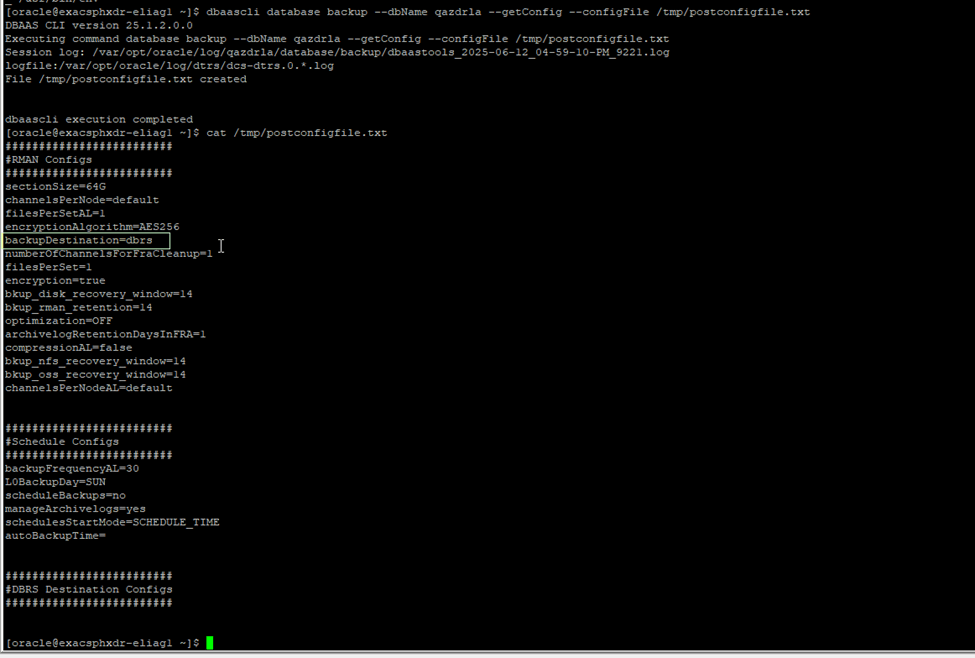
This confirms the migration from Object Storage to Autonomous Recovery Service.
Verify TNS Entries
• Check if new TNS entries are added for ZDRLA appliances.
• Look for the following in the TNS admin directory:
IFILE=/var/opt/oracle/dbaas_acfs/qazdrla/dbrs/tnsnames.ora
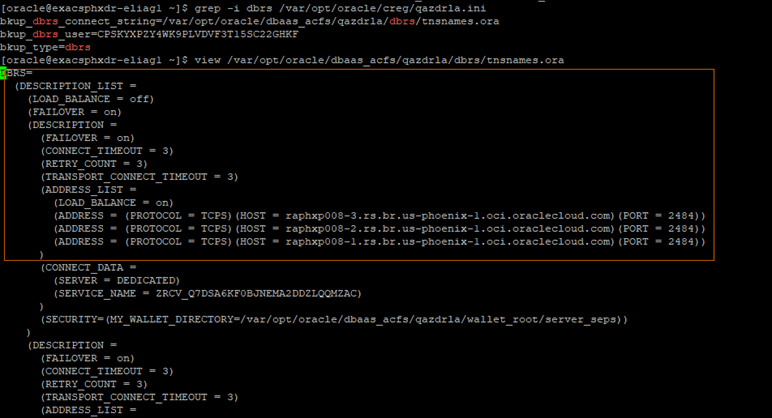
Presence of this file confirms the database is now configured to use ZDLARS connectivity.
Validate Backup Execution
- Navigate to the Backups section.
- Confirm new backups are completing successfully under Autonomous Recovery Service.
Optional: Enable Retention Lock (Highly Recommended)For enhanced ransomware protection – Immutable Backup
Step 1 – Create a New Backup Policy
- Go to Backup Policies
- Create a new policy
- Enable Retention Lock
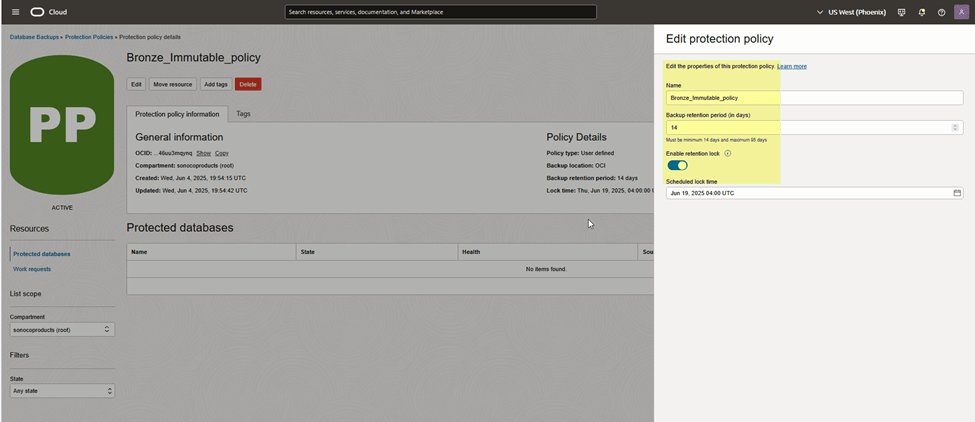
Retention Lock ensures:
- Backups cannot be modified
- Backups cannot be deleted
- Protection remains enforced until retention period expires
Step 2 – Apply the Policy
Assign the retention-locked policy to your database backup configuration.
This is especially critical for:
- Healthcare organizations
- Financial services
- Regulated industries
- Enterprises concerned about insider threats
Why This Matters
Traditional backups protect against hardware failure.
ZDLARS protects against:
- Ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
- Accidental deletion
- Regulatory non-compliance
- Data corruption
By separating backup storage into an isolated fault domain and enforcing immutability, Oracle significantly reduces recovery risk.
Final Thoughts
Enabling Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service is one of the most impactful security upgrades you can implement in OCI for Oracle databases. It transforms backup from a passive safety measure into an active cyber-resilience strategy.
If you’re managing production workloads in OCI, especially mission-critical systems, this configuration should be part of your standard database hardening checklist.
Source
Overview of Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery ServiceZero Data Loss Recovery | OracleIntroducing the Oracle Database Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service
